User guide
A central module of the toolkit is the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator. With several hundreds of measurement tools, methods and services available to assess and measure impacts on sustainable development – how do you choose the one that fits your needs best? The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator addresses this challenge. It is a unique service for businesses that want to measure and manage their impact on sustainable development. This user guide provides detailed information on the tool navigator and its functionalities.
In just three steps the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator helps you explore and find tools that are fit for your specific situation. On top of generating a selected list of tools that fit your requirements, the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator provides additional information on the tools, their accessibility and their features, that will help you make informed choices.
Contents
An introduction to the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator
In January 2016, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) entered into force, representing the global sustainable development objectives and aspirations for 2030. The United Nations General Assembly adopted this unprecedented global sustainable development agenda in late 2015 and for the first time, business was represented at the negotiation table. Business has now become an important partner in solving the most pressing challenges of our century. And indeed, the scope and ambition of the global goals requires the active participation of all societal actors, including business, if they are to be achieved.
As noted by the UN Global Compact, “The SDGs hold the potential to guide companies in their long term investments, strategic prioritization and goal setting. Whereas all SDGs may not be relevant to every company, there is a strong and proven business case for companies to contribute to the realization of each SDG.”
The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator supports managers and stakeholders in the evaluation of currently existing tools that help companies demonstrate their contribution to achieving the SDGs.

What is the Global Value tool navigator?
The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator is a unique service for businesses that want to measure and manage their impact on sustainable development. It helps managers and stakeholders evaluate the capabilities, features and coverage of SDG issues of the plethora of currently existing impact measurement and management tools. It allows systematic filtering of more than 220 tools, methods and frameworks.
The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator is a simple to use and easy to navigate online tool. In just three steps the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator helps companies explore and find tools that fit their specific situation, address the part of the value chain they wish to analyse and cover their material sustainability issues. By selecting certain criteria within three predefined filter options, the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator helps to navigate the abundance of available tools. The more specific the selection of criteria the more targeted results the user will receive. 
Who is the Global Value tool navigator for?
The objective of the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator is to support companies in contributing to a sustainable world. It was designed with a focus on businesses of any size and sector who wish to measure and manage their impacts on sustainable development and to progressively integrate the SDGs.
Other organizations, consultants and stakeholders are also encouraged to use it to identify appropriate tools for specific needs, to gain knowledge on sustainability issues and on how to assess and manage impacts on society and environment.
The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator will also be useful to tool developers, as it provides an overview of existing tools, visualizes how these tools perform in comparison to others and thus creates market transparency.
The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator is equally suitable for experienced users of assessment and management tools as well as for people who are just starting to deal with sustainability issues and the impacts organisations or companies can have on society.

Why use the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator?
Here are 5 good reasons to use the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator:
1. It delivers fast and targeted results from a database of more than 220 tools and methods at no charge: With plenty of tools, methods and services in existence that claim to assess and measure impacts on sustainable development – how do you choose the one that fits your needs best? The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator provides you with the necessary information. In just three steps it filters out the relevant tools from a unique database of more than 220 tools and methods. It delivers fast and targeted results and provides the most important information and features of a tool at a glance. As the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator was developed by an independent research consortium, it represents no commercial interests and can provide all the information at no charge.
2. It delivers fit for purpose assessment tools: The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator helps companies to select the most appropriate tool for the intended purpose. It provides companies and stakeholders with knowledge on how to assess and manage impacts, on how to mitigate negative and maximize positive effects on sustainable development and on how to implement this knowledge into management practice and strategy.
3. It is built on three years of target-oriented research on corporate impact measurement and management: The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator is a service which was developed within one of the largest EU research projects on CSR, the GLOBAL VALUE Project. It draws on three years of target-oriented research on corporate impact assessment and management by an independent research consortium.
4. It draws on the expertise of more than 250 international experts: the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator draws on the expertise of more than 250 international experts. The GLOBAL VALUE project was implemented by eleven research institutions, civil society organisations and companies. The consortium includes some of the leading minds in CSR and development research across Europe, Asia and Africa. In addition the project established the GLOBAL VALUE expert crowd with more than 250 experts representing policy, civil society organisations, business, and academia perspectives that were consulted in collecting the tools available in the database.
5. It has an easy-to-use interface: With the broad variety of assessment tools available it can seem as an unmanageable task to find the one tool that fits your requirements best. The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator’s biggest advantage is, that it provides an easily managed solution to this seemingly invincible search for the needle in the haystack. It consists of an easy-to-use online platform where the user is simply asked to select certain criteria within three predefined filter options. The remaining search is done by the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator. It filters out the relevant tools from the database and provides targeted results containing the most important information at a glance.
Step 1: Getting started - how to access the navigator
The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator is available here. You will be directed to the landing page.
Landing page
As non-registered user you will be granted limited access to the tool navigator. This means the output of each search will be limited to a maximum of 5 results. To gain full access to the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator and to be able to view the complete list of results as well as to access the expert consultation, we kindly ask users to register to the GLOBAL VALUE user area.
In case you wish to receive limited access to the preview of the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator, please proceed with Step 2.
If you are new to the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator, please register with your full name, e-mail address and affiliation here. Please remember to accept the terms and conditions by activating the check box. You will receive a confirmation e-mail within a few minutes.
If you are already registered, please enter your e-mail address and password to proceed to Step 2. In case you have lost your password, please enter your e-mail address, leave the password field blank and press Login. Your password will be sent to you by e-mail within a few minutes.
For technical assistance, please contact us at contact@global-value.eu.
Example
John Doe, CSR Manager of XY Textiles Ltd registers to the navigator
Step 2: Searching the navigator - how to use the filter menu
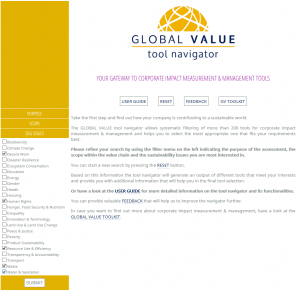
Once you are registered and logged in, you will be directed to the landing page here. In order to filter the database of tools included in the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator, you have three filter options available to you in the menu on the left hand side. Please refine your search by using the filter options in the menu and indicate the purpose, scope and issues that the tool(s) you are interested in should cover.
To support you in the usage of the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator you can switch back and forth between the navigator and this user guide. You can always start a new search by pressing the Reset button, provide valuable Feedback to the team behind GLOBAL VALUE, or visit the GLOBAL VALUE toolkit for comprehensive information about corporate impact measurement and management.
Landing page
Set filter options and select criteria
Please start your search by indicating the purpose of assessment. You have three criteria available to you. Choose one of the three options by ticking the respective check box. Only a single choice is possible.
Information & Learning
Tools with this purpose support companies in learning about sustainability issues and potential impacts. Typical tools in this category
are:
Guidelines, such as the UNGC’s Guidance on responsible business in conflict-affected and high-risk areas,
Frameworks, such as Transparency International’s Assurance Framework for Corporate Anti-Bribery Programes, and
Training tools, such as the WBCSD’s Eco-efficiency learning module.
Reporting
Tools with this purpose help companies to collect, structure and share sustainability information with stakeholders. Typical tools in this category are:
Standards, such as the Global Reporting Initiatives’s GRI Standards,
Reporting frameworks, such as the IIRC’s International Integrated Reporting Framework, and
Indicator sets, such as the GIIN’s IRIS Catalogue of Performance Metrics.
Management Control
Tools with this purpose support companies in achieving management objectives, weighting strategic options, and identifying improvement measures. Typical tools in this category are:
Valuation tools, such as the IFC’s Financial Valuation Tool,
Strategy tools, such as the WBCSD’s Measuring Impact Framework, and
Self-assessment questionnaires, such as the Global Compact Self Assessment Tool.
Example
John is searching for a tool that will help him find out what impacts XY Textiles Ltd has in the producing countries, how he can reduce negative impacts and increase positive ones. He therefor marks “Management control”
Great – you’ve got purpose! Now select the scope that your preferred tool should cover. You have five criteria to choose from. Please select one option by ticking the respective check box. Only a single choice is possible.
Project
A project is a target-oriented set of tasks, with clear delimitations in terms of time and resources invested. Typical tools are:
The London Benchmarking Group’s LBG Model, and
True Impact’s Board Service ROI Tracker.
Product
Product assessments may cover one, several or all steps of the product’s life cycle. Typical tools are:
The Carbon Trust’s Footprint Expert 4.0, and
The RPSM’s Handbook for Product Social Impact Assessment.
Company
This category covers the entire, generally for-profit, organization. Typical tools are:
B Lab’s B Impact Assessment, and
The Gender Equality Principles Initiative’s Gender Equality Principles Assessment Tool.
Production site
Tools with this scope focus on local impacts from factories or other production sites, including community impacts. Typical tools are:
Impact Measurement Ltd.’s Impact Predictor, and
Oxfam’s Poverty Footprint.
Supply Chain
The supply chain includes the entire network of organizations involved in sourcing, processing, manufacturing, distribution and disposal. Typical tools are:
APIC’s SCOR Model, and
Sedex’ Supply Chain Risk Assessment.
Example
John is searching for a tool that will help him find out what impacts XY Textiles Ltd has in the producing countries and therefor marks “Production site”
Almost there! Please choose at least one from among the 23 sustainability issues available by ticking the respective check box. Multiple choice is possible.
Biodiversity
Climate Change
Decent Work
Disaster Resilience
Ecosystem Conservation
Education
Energy
Gender
Health
Housing
Human Rights
Hunger, Food Security & Nutrition
Inequality
Innovation & Technology
Land Use & Land Use Change
Peace & Justice
Poverty
Product Sustainability
Resource Use & Efficiency
Transparency & Accountability
Transport
Waste
Water & Sanitation
Why these 23 issues? We derived these issues directly from the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As an interconnected agenda including 17 global goals and 169 targets, the SDGs can be difficult to navigate. We have done the job for you by breaking them down into 23 key sustainability issues for business.
Example
As XY Textiles Ltd has production sites in Bangladesh, John is particularly interested in social impacts (Human right, Decent work) and environmental impacts (Resource use & efficieny, waste, water & sanitation)
Step 3: Getting results - how to interpret the output page
After setting your filter criteria, please press Submit.
You made it! The GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator now displays a list of tools that fit your filter criteria. The filter criteria are displayed in the menu on the left hand side. You can always reset your criteria and start a new search by pressing the Reset button, provide valuable Feedback to the team behind GLOBAL VALUE, or visit the GLOBAL VALUE toolkit for comprehensive information about corporate impact measurement and management.
Results
The top bar on the output page indicates the number of tools in the database that fit your filter criteria. Below, your results appear in alphabetical order. Only the first 5 tools are displayed. To see the full list of results, please scroll to the bottom of the page and press View Complete List. Or, in case you are using the preview version with limited access to the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator, press Login or register with Global Value to see the complete list of tools.
For each tool, the output page provides additional information that will help you in choosing the tool that best fits your needs.
1. Tool name, developer and URL. Clicking on the name of the tool will re-direct you to the tool website.
2. Tool description. This short text provides a brief description of the tool’s features
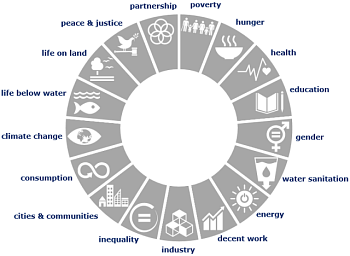
3. SDG wheel. This graph shows you how many and which SDGs are covered by the tool. Clicking on the wheel will direct you to a bigger version of the wheel and the explanation on what the SDG wheel indicates.
4. Symbol bar. The symbol bar provides a quick overview of the main features of the tool (purpose, scope, output, requirements & acessibility).
The SDG wheel
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are an interconnected agenda including 17 global goals and 169 targets. We have broken them down into 23 key sustainability issues for business in the filter menu.
On the output page, the GLOBAL VALUE tool navigator translates these issues back to the SDGs. Therefore, it can show you which SDGs are addressed by the respective tools. This is what the SDG wheel is for.
Each segment of the SDG wheel represents one of the 17 SDGs. The colours and symbols refer to the official SDG markings. The text on the side of each segment refers to the main topic of the particular SDG. The information in the SDG wheel indicates whether an SDG or at least one of its targets are addressed by a certain tool. It does not indicate to what depth these are covered. Thus, the SDG wheel does not serve as evaluation on how well a tool covers certain SDGs and targets. When a tool addresses a certain SDG, the segment is coloured. When a tool does not address a certain SDG, that segment is marked in grey. In some cases, tools may focus on providing a methodology or process for impact measurement and management, without clear reference to sustainability issues. In such cases, no clear identification of SDGs or their targets can be made. In these cases, the SDG wheel remains grey. For instance:
(1) All segments coloured (B Impact Assessment)

The B Impact Assessment is an online self-assessment tool for assessing a company’s overall performance in the areas of governance, workers, community & environment. The questions address at least one target of each of the SDGs. This does not mean that all SDGs have the same importance in the assessment. It only indicates that at least one target of every SDG is represented.
(2) Some segments coloured (HRCA Quick Check)
The Quick Human Rights Compliance Assessment – a diagnostic online self-assessment tool to assess the impact of business operations on people and human rights – addresses 10 out of 17 SDGs. The SDG wheel indicates that the tool addresses at least one target of SDG 1 (poverty), 2 (hunger), 3 (health), 4 (quality education), 5 (gender), 6 (water sanitation), 8 (decent work), 10 (inequality), 16 (peace & justice), and 17 (partnership).
(3) All segments grey (WBCSD MIF)
For the WBCSD Measuring Impact Framework – a tool that helps companies evaluate where and how they can contribute to the development issues of the country they are operating in – no general presentation of SDG coverage can be produced as SDG coverage entirely depends on what issues or SDGs the users of the tool choose for the assessment and what they think the most important issues in the region are.
The symbol bar
The icons in the symbol bar shows you the features of each tool at a glance. The symbol bar provides additional information on the tool and its features that will help you in the final tool selection. The following table provides an overview of the purpose and meaning of each icon. A short signifier for each icon also appears as you hover your mouse over an icon.
(1) Purpose: Indicates what the ultimate goal of the assessment is. You already know these criteria from the filter menu.

Information & Learning:
Tools which serve the primary goal of supporting the company in learning about its impacts/issues, understanding what the impacts are and where in the value chain they are caused. A learning tool refers to a framework or a guideline that provides useful information while or before taking an assessment.

Reporting:
Tools which serve the primary goals of providing and sharing information for stakeholders, third parties or other interested parties.

Management control:
Tools which serve the primary goal of supporting the company in weighting strategic options, finding the best alternative in terms of measuring and managing impacts.
(2) Scope: Indicates which part of the value chain should be analysed. You already know these criteria from the filter menu.
Project:
Tools which can be applied for measuring and/or managing impacts of projects.
Product:
Tools which can be applied for measuring and/or managing impacts of a product or service that results from a (production) process. Can include impacts from product use and disposal.

Company:
Tools which can be applied for measuring and/or managing impacts of companies as a whole.
Production site:
Tools which can be applied for measuring and/or managing impacts locally resulting from a production site including impacts on the community affected.
Supply chain:
Tools which can be applied for measuring and/or managing impacts that take place in the company supply chain, addressed procurement and sourcing issues.
(3) Output: gives an indication on what kind of output a user can expect from the tool at the end of the assessment.

Score:
By the end of the assessment the user receives a score or index indicating the performance level.

Report:
By the end of the assessment the user receives a result in form of a report or text (e.g. recommendations for improvement, report).
Dashboard:
By the end of the assessment the user receives visual illustration (e.g. graph, dashboard, bar chart, scoreboard) summarizing a general overview of the performance.

Benchmark:
By the end of the assessment the user will be able to benchmark his performance against other businesses.

Monetary value:
By the end of the assessment the user will receive an indication on the monetary value of its impacts.
(4) Requirements: Gives an indication on what kind of additional requirements might be needed during the assessment.

Stakeholder involvement:
Indicates whether the assessment requires stakeholder involvement.

Quick assessment:
Indicates whether the assessment requires very little time (up to one week).

External assessment/service:
Indicates whether the assessment is done by a third party e.g. external evaluation of companies provided and conducted by independent actos (ratings, indices).
(5) Access: Gives and indication on how the tool can be accessed before the assessment.

Access:
Indicates whether access to the tool is restricted. In this case the user will have to actively apporach the provider of the tool to receive more information on how to gain access to the tool

Costs:
Indicates whether the usage of the tool requires a payment at some point of the assessment.
![]()
Impressum
André Martinuzzi, Norma Schönherr, Adele Wiman & Patricia Schindler
© 2017 Institute for Managing Sustainability │ Vienna University of Economics & Business
contact@global-value.eu
www.global-value.eu/toolkit
![]()
Disclaimer
GLOBAL VALUE is co-funded by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme under grant agreement no 613295. Sole responsibility for the project lies with the participating organisations. The European Commission is not responsible for the use that may be made of any material arising from this project.
Use of this site is subject to the Terms & Conditions of Use